Loss of control and collision with terrain
ASAP Avionics Services Ltd.
Robinson R44 Astro, C-FMBO
Campbell River, British Columbia
The Transportation Safety Board of Canada (TSB) investigated this occurrence for the purpose of advancing transportation safety. It is not the function of the Board to assign fault or determine civil or criminal liability. This report is not created for use in the context of legal, disciplinary or other proceedings. See Ownership and use of content. Masculine pronouns and position titles may be used to signify all genders to comply with the Canadian Transportation Accident Investigation and Safety Board Act (S.C. 1989, c. 3).
History of the flight
On 01 October 2017, at 1530,Footnote 1 the ASAP Avionics Services Ltd. Robinson R44 Astro helicopter (registration C-FMBO, serial number 0106) (Figure 1), departed from the Campbell River Airport (CYBL), British Columbia, during daylight hours, with 2 pilots on board. The purpose of the flight was to allow the pilot in the right-hand seat to demonstrate his ability to conduct slow flight manoeuvres for potential future employment.
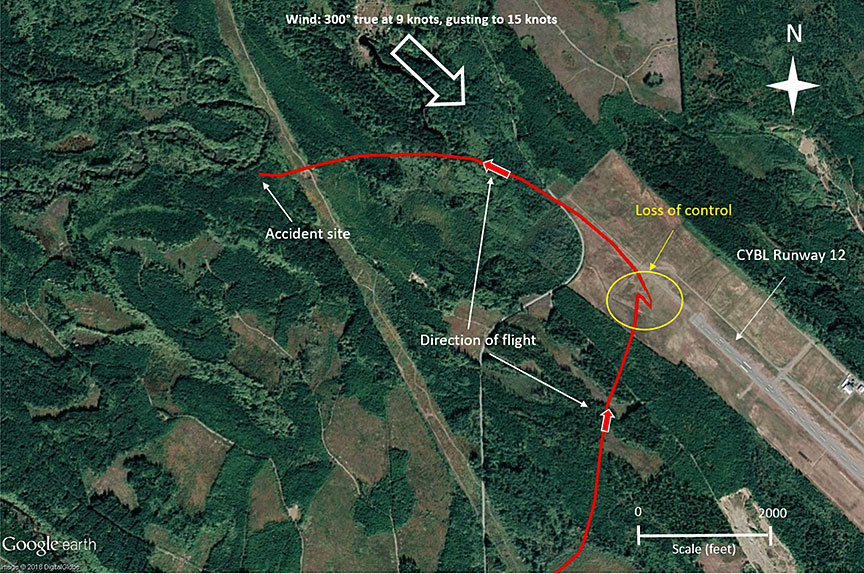
At 1548, after conducting a number of flight exercises about 5 nautical miles (nm) to the northwest of the airport, the flight crew contacted the NAV CANADA flight service station at CYBL and informed them that the helicopter would be returning to the airport infield area west of the threshold of Runway 12 (Figure 2) to conduct hover exercises.
At 1553, while on final approach to CYBL, control of the helicopter was transferred from the right-seat pilot to the left-seat pilot for the demonstration of a manoeuvre. Shortly after the control transfer, while in close proximity to the ground at slow speed, the helicopter began to spin uncommanded to the right. After several revolutions, it travelled in a northwesterly direction away from the airport. During that time, it attained an altitude of approximately 150 feet above ground level (AGL) and approximately 85 knots groundspeed.
At approximately 1555, the helicopter collided with trees about 1.2 nm northwest of Runway 12. The damage to the helicopter, trees, and terrain indicated that the aircraft had been on a relatively level flight path when it first struck the trees. It had then pitched to a steep nose-down attitude and struck the ground in a vertical profile. Analysis of the wreckage indicated that the rotor had been turning during the first impact with the trees and was still turning, though at a slower rate, on final impact with the terrain. After coming to rest, the helicopter's engine continued to run for an undetermined period. The left-seat pilot was fatally injured, and the right-seat pilot was seriously injured. The helicopter was destroyed. There was no post-impact fire.
At 1656, approximately 1 hour after the accident, the surviving pilot was able to contact 911 on his personal cellphone, and a search was initiated.
At 1712, an emergency locator transmitter (ELT) signal was detected by the flight service station.
At 1806, search-and-rescue personnel arrived on scene. The surviving pilot was evacuated from the accident site at 1948.
Pilot information
Both pilots were certified and qualified for the flight.
| Left-seat pilot | Right-seat pilot | |
| Type of licence | Airline transport pilot licence – helicopter | Commercial licence – helicopter |
| Medical expiry date | 01 June 2018 | 01 August 2018 |
| Total flying hours | 3116 | 122 |
| Type ratings | RH22, RH44, BH06, MBK7 | RH44, BH06, HU30 |
| Total hours on type | 738 | 27 |
| Hours, last 7 days | 1 | 0 |
| Hours, last 30 days | 4.8 | 0 |
| Hours, last 90 days | 24.6 | 0 |
Meteorological information
The aviation routine weather report (METAR) for CYBL at 1500 indicated the following: winds 300° true (T) at 9 knots, gusting to 15 knots, varying from 270°T to 340°T; visibility 30 statute miles; few clouds at 4000 feet AGL; temperature 18 °C; dew point 5 °C; and altimeter setting 30.14 inches of mercury.
Aircraft information
The helicopter was certified, equipped, and maintained in accordance with existing regulations and approved procedures. It had no known deficiencies and was being operated within its weight-and-balance and centre-of-gravity limits. The helicopter was not equipped with a flight data recorder or cockpit voice recorder, nor were these required by regulation.
| Manufacturer | Robinson Helicopter Company |
| Type, model, and registration | R44, Astro, C-FMBO |
| Year of manufacture | 1994 |
| Serial number | 0106 |
| Certificate of airworthiness | 13 January 2007 |
| Total airframe time | 2779.1 |
| Engine type (number of engines) | Lycoming O-540-F1B5 (1) |
| Maximum allowable take-off weight | 1088.62 kg |
Technical examination
A comprehensive laboratory examination of C-FMBO was performed. Representatives from the helicopter manufacturer (Robinson Helicopters) and engine manufacturer (Lycoming Engines) were present for the examination, in addition to investigators from the TSB and the U.S. National Transportation Safety Board.
Flight control and drivetrain
Flight control continuity was confirmed, and none of the flight control components showed signs of disconnect or premature failure. The main and tail rotor gearboxes, as well as the engine freewheel unit, were examined, and no malfunction or pre-existing anomaly was noted.
Engine
The engine was found to be capable of producing full power and was within normal operating specifications for its type.
Engine–to–main transmission coupling
To transfer engine power to the main transmission, the R44 helicopter employs 4 double-V drive belts running around 2 sheaves—the lower, "driving" sheave and the upper, "driven" sheave.
An examination of the drive belts showed evidence of slippage and wear. One of the belts had a considerable amount of glazing and heat damage, with the web between the belts separated in areas. Another belt was damaged more significantly, with one of the strands burned completely through and the remaining strand distorted and inconsistent. The damage observed on the belts is consistent with the belts having moved from their proper location on the sheave and subsequently being subject to loading either on the sheave or in contact with rotating parts. However, the investigation was unable to determine how much, if any, of the damage occurred prior to the impact with terrain.
Engine-cooling fan
The engine is cooled by means of an engine-cooling fan, which is attached to the engine by a taper-fit between the end of the drive shaft and the socket of the fan. Examination of the tapered surface of the shaft and bearing assembly showed some significant gouging damage. It was also noted that the bolts holding the fan wheel to the socket hub were loose. Further examination revealed that the fan wheel bolt holes were elongated. The investigation was unable to determine if the loose bolts and elongated holes contributed to the occurrence.
Emergency locator transmitter
On examination, the ELT was found to be intact. The unit had activated and emitted a signal that was detected by the CYBL flight service station approximately 80 minutes after the accident.
Conclusion
In this accident, the left-seat pilot was fatally injured, and the right-seat pilot was seriously injured. Both pilots were certified and qualified for the flight. The weather conditions were not considered a factor in the accident. The aircraft was maintained and certified in accordance with existing regulations.
The cause of the loss of control and collision with terrain could not be determined. As this and other occurrences have demonstrated, when cockpit or data recordings are not available to an investigation, the identification and communication of safety deficiencies to advance transportation safety may be precluded.
The Board has previously recommended that
the Department of Transport require the mandatory installation of lightweight flight recording systems by commercial operators and private operators not currently required to carry these systems.
Transportation Safety Recommendation A18-01
This concludes the TSB's limited-scope investigation into this occurrence. The Board authorized the release of this investigation report on 06 June 2018. It was officially released on 11 June 2018.